Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a condition affecting up to 5% of the adult population. It can cause muffled hearing, pain in the ear, and other symptoms. Untreated, long term eustachian tube dysfunction can have serious health consequences, including damage to the eardrum and middle ear. Dr. Shervin Aminpour uses Acclarent AERA Eustachian Tube Dilation System to treat persistent Eustachian tube dysfunction at the source.
Eustachian Tubes and Their Functions
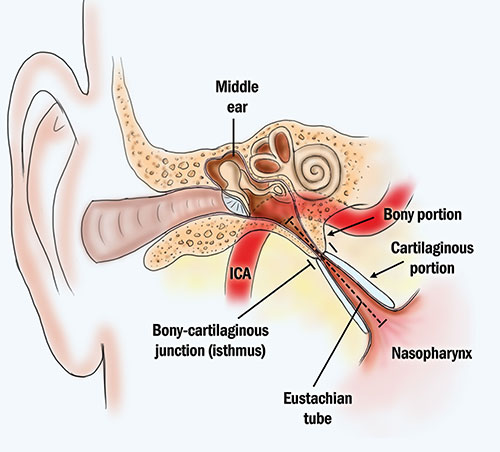
The Eustachian tubes are the narrow tubes that connect the middle ear (the space behind the eardrum) with the back of the nose. In adults, these tubes are approximately 3 to 4 cm (1.18 to 1.57 inches) long. The 3 main functions of the Eustachian tubes are to:
- Ventilate the middle ear;
- Protect the middle ear from disease; and
- Help drain secretions away from the middle ear.
The Eustachian tubes are normally closed, but open when we yawn, swallow, or chew, which allows air to flow into the middle ear and mucus to flow out. This equalizes air pressure on either side of the eardrum and keeps the middle ear free of mucus. It also helps the eardrum vibrate, which is necessary for us to hear. As long as the Eustachian tubes are working properly, they typically go unnoticed.
Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
ETD occurs when the Eustachian tube becomes blocked or fails to open properly. As air cannot get into the middle ear, the air pressure becomes unequal, with greater pressure on the outside of the eardrum than on the inside, in the middle ear. This pressure pushes the eardrum inward, so it becomes tense and does not vibrate properly when it is hit by sound waves.
Symptoms of ETD can last for several hours to several weeks or longer. They may include:
- Dull or muffled hearing
- Ear pain
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
- Dizziness
Causes of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Conditions that cause ETD include:
- Common cold and other nasal, sinus, ear, or throat infections: Blocked nasal passages and thick mucus with a cold or infection can block the Eustachian tube and cause ETD. Infection can also cause inflammation and swelling of the lining of Eustachian the tube. ETD symptoms can persist for a week or more after a cold or infection has healed, as trapped mucus and swelling can take some time to resolve.
- Glue ear: This is a condition, common among children, in which the middle ear becomes filled with a glue-like fluid. The Eustachian tube becomes congested, so air cannot flow into the middle ear. This creates a difference in air pressure, which can lead to muffled hearing and pain. The glue-like fluid further interferes with the vibrations of the eardrum, which can further affect the hearing.
- Allergies: Hay fever or persistent rhinitis (inflammation of the nose), that come with a blocked, itchy, runny nose and sneezing, can cause extra mucus and inflammation in and around the Eustachian tubes. This can lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Blockage of the Eustachian tube: Enlarged adenoids or any condition that causes a blockage in the Eustachian tubes can lead to ETD. In rare cases, tumors that develop in the back of the nose can cause ETD.
How Eustachian Tube Dysfunction is Diagnosed
An ENT diagnoses ETD by ordering certain tests. In most cases, the common procedure to detect ETD is a nasal endoscopy and at times, tympanometry.
ETD is also diagnosed with the help of CT scans. The doctor also carries out a head and neck exam to check whether the patient experiences any issues due to a fluid imbalance in the ear.
Los Angeles Allergy Specialist
Dr. Aminpour has a vast amount of knowledge and experience when it comes to allergies and how to treat them. Learn more about the many symptoms and what treatments we have to offer.
Learn MoreTestimonials
Complications of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
In many cases, after a cold, for example, ETD will resolve on its own within a few days to a week or so after the infection clears up. However, persistent ETD should not be left untreated. It can have serious complications, including:
- Otis media with effusion (a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear)
- Atelectasis of the middle ear (reduction in middle ear volume caused by Eustachian tube blockage followed by absorption of the oxygen in the middle ear and retraction of the ear drum medially)
- Adhesive otitis (inflammation of the middle ear caused by prolonged ETD resulting in permanent retraction of the eardrum and obliteration of the middle ear space)
- Cholesteatoma (abnormal, noncancerous skin growth behind the ear drum caused by repeated ear infections)
- Perforation of the ear drum
Risk Factors of ETD
A blocked Eustachian tube can cause imbalance and dizziness since the Eustachian tubes are responsible for equalizing the ear pressure. In addition, it can lead to a loss of hearing and cause blocks in the ear that leads to a ringing sensation.
Blocked Eustachian tubes can also cause upper respiratory tract infections which can eventually lead to a loss of hearing.

When should I see my doctor?
In most cases, ETD goes away on its own. Home remedies like forcing a yawn or chewing gum are helpful in getting rid of the blocked air in the tubes.
If you begin to experience symptoms such as ringing in the ears, dizziness, or loss of hearing, it is important to make an appointment with an ENT right away.
Treatments for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Mild cases of ETD can be treated using over the counter medications. Patients are often prescribed anti-histamines in cases where the ETD is triggered by allergies.
Severe infections are treated using antibiotics and topical treatments.
A common treatment method is the Eustachian tube balloon dilation method. In this method, the surgeon inflates a small balloon into the Eustachian tube through the nose. The inflated balloon clears a passageway for mucus and air. Once this is achieved, the surgeon deflates the balloon and pulls it back. This restores the proper function of the Eustachian tube.
Acclarent AERA System to Treat Persistent Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
In the past, treatments for chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction were limited primarily to medications or surgery, but Dr. Aminpour offers his patients another option. The Acclarent AERA Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation System is the first device in the U.S. for dilating the Eustachian tube to treat persistent ETD.
With this system, Dr. Aminpour uses a catheter to insert a small balloon through the nose and into the Eustachian tube. The balloon is inflated to open up a pathway for air and mucus to flow through the Eustachian tube, to help restore normal function. After the Eustachian tube has been dilated, the balloon is deflated and removed.
Clinical studies of the Acclarent AERA system have shown a 99.7% technical success rate in Eustachian tubes dilated and a greater rate of ear drum normalization than in patients treated with medical management alone. There were no device or procedure-related serious adverse events reported, and a significant percentage of patients reported improved quality of life. The Acclarent AERA system is at the forefront of Eustachian tube dysfunction medical technology and will play a significant role in treating this disease.
Dr. Shervin Aminpour is a board-certified otolaryngologist – an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctor in Los Angeles – and a sinus surgeon who offers a broad range of services for patients suffering from ear, nose, and throat issues, such as Eustachian tube dysfunction. He stays up-to-date on ever-changing and evolving ENT technology to provide his patients with the most advanced treatments and highest quality care.
Dr. Aminpour is a certified Los Angeles allergist trained in the Acclarent AERA Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation System. If you are suffering from persistent Eustachian tube dysfunction, it is important to receive medical treatment for your condition to help prevent further serious complications. When you come to our clinic for a consultation with Dr. Aminpour, he can evaluate your condition and advise you if the Acclarent AERA system is the right treatment option for you.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction FAQ
What is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Eustachian tubes connect the middle ears to the upper throat. When functioning properly, the tubes drain fluid and keep pressure equalized in the ear. Eustachian tubes remain closed the majority of the time, but open when chewing, swallowing or yawning. When tubes open, negative pressure or fluid can enter the tube. When the tubes become blocked, the pressure outside the ear is high, making hearing difficult. Patients also tend to experience an overwhelming sensation of “fullness” in the ear. This dysfunction can be extremely painful.
What are the Common Symptoms of EDT?
- Ear pain
- A feeling of fullness
- Ear feels plugged
- Ringing or popping noises
- Struggle to hear clearly
- Dizziness
- Itching inside of ear
Will EDT Go Away on its Own?
EDT can resolve itself on its own without requiring treatment. If you struggle with the symptoms of EDT in Burbank after for several days, get help from Dr. Shervin Aminpour.
Do Steroids Help Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Allergies can play a significant role in chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction. There are numerous ways to treat allergies, including steroids. Oral and nasal steroids may have a beneficial effect and can be used to reduce the inflammation and swelling of the Eustachian tube.
Are There Home Remedies for EDT?
If Eustachian tube dysfunction affects you, there are many home remedies that may or may not be helpful. While your mouth is closed, try breathing out of your nose. If you suffer from allergies, they could be the link to your struggle with Eustachian tube dysfunction. Antihistamines can an effective treatment to clear the sinus passages and prevent any blockage in the ear that might affect the Eustachian tubes. Over the counter medications may be effective in reducing the pain or discomfort if an ear obstruction is present.
How Does Altitude Change Affect Eustachian Tube Dysfunction or Blockage?
Air travel can result in discomfort to the Eustachian tubes due to the sudden changes in altitude or air pressure. Moving from low atmospheric pressure at high elevations to landing where the pressure is higher can create very painful symptoms. Many people experience ear popping when a flight is taking off or landing. The popping occurs because a small air bubble was trapped in the Eustachian tube. The most common way to avoid any issues with the ear is to chew gum during takeoff or landing. Other ways to equalize pressure include yawning, swallowing or sucking on a piece of candy. Those with a more serious case can suffer extreme pain and should have the condition treated and resolved prior to taking a flight.
What is Patulous Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
The term Patulous means continuously open. Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs when the Eustachian tube never closes. If you can hear echoing when you talk, or hear yourself breathe, you may be suffering from Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction. This distortion of sound is because your voice is traveling up your Eustachian tubes at a faster rate than out the ear and into the room itself. If you wish to learn more about Eustachian Tube Dysfunction or Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Shervin Aminpour today.